A practical, step-by-step guide with prerequisites, commands, troubleshooting, and a printable checklist. This covers Dell iDRAC (6→9) and common BMC/IPMI implementations (Supermicro IPMI / IPMIView), plus RACADM and IPMI web-ISO methods – based on vendor docs, community troubleshooting and up-to-date how-tos. Key references are cited at important points.
Quick summary (what this lets you do)
Virtual Media (a.k.a. “virtual CD/DVD” or “mount ISO” via the BMC) lets you present an ISO image on your workstation or an HTTP/NFS share as if it were a local CD-ROM plugged into the server. You can then boot the remote server from that ISO and install or repair an OS without physical media.
Table of contents
- What “virtual media” is (short)
- Things you’ll need (hardware, files, network)
- Prechecks & BMC/Bios settings
- iDRAC (Dell) — step-by-step (GUI + RACADM)
- IPMI / Supermicro — step-by-step (web UI and IPMIView)
- Mounting ISOs from local file, HTTP(S) or NFS
- Common problems & fixes (Java, JNLP, blank screen, speed)
- Security considerations and best practices
- Troubleshooting checklist & quick commands
- Printable checklist and references
1 — What “virtual media” actually is
Virtual Media is a feature of server BMCs (iDRAC, IPMI, IMM, iLO, etc.) that maps a remote ISO (from your PC or a network share) into the server’s virtual USB/CD-ROM so the server can boot/install from it. It works via the remote console session (Java/JNLP or HTML5 console) or via BMC CLI (for some vendors).
2 — What you’ll need before starting
Hardware & files
- Admin credentials for the BMC (iDRAC/IPMI) and IP address.
- The bootable ISO you want to install (local file) or a reachable HTTP(S)/NFS/SMB location.
- A client workstation with a supported browser (and optionally Java or the vendor console app).
Network & access
- TCP access to the BMC IP and required ports (see Ports section).
- Reliable network throughput — ISO installs transfer many GBs; slow links will increase install time.
Software
- iDRAC: modern iDRAC versions provide an HTML5 Virtual Console; older ones used Java/JNLP.
Supermicro IPMI: IPMIView or browser + Java; some older BMCs rely on Java applets or IPMIView which can be brittle.
3 — Prechecks & BMC/Bios settings (do this first)
- Confirm BMC IP and admin account. If you don’t have network access, set a static IP or use DHCP console.
- Verify BMC firmware is reasonably current – virtual media and remoteimage features are improved/fixed in newer firmware. (If you can, note firmware version.)
- Ensure BIOS boot order allows USB/virtual CD-ROM or that you can interrupt boot order to select the virtual device.
Confirm required firewall ports (iDRAC commonly uses 443 and VNC ports for console); open them if needed.
4 — iDRAC (Dell) — step-by-step
A. GUI (HTML5 / Virtual Console) — common, recommended path
- Step 1 – Open browser → https://<iDRAC-ip>/ → log in with admin account.

- Step 2 – Click Launch Virtual Console (or Console/Media). Newer iDRACs will open an HTML5 console; older ones may download a launch.jnlp file (Java Web Start).

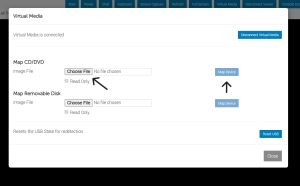
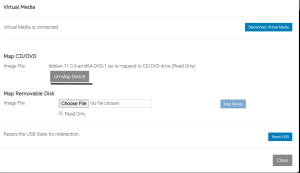
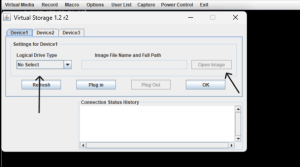
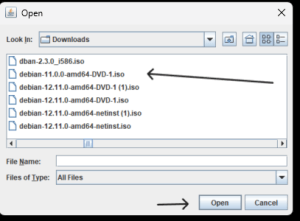
- Step 3 – In the console window, find Virtual Media (or Connect Virtual Media). Choose Map CD/DVD or Mount → Choose Local File and select your ISO, or choose to mount from HTTP/HTTPS/NFS if available.

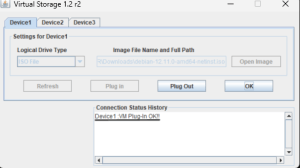
- Step 4 – After mounting, reboot the server and choose the virtual CD/USB boot device, or use one-time boot menu (F11/F12) to boot the ISO.

- Step 5 – Proceed with the OS installation as if the ISO were physical media.
B. Command line – racadm remoteimage (useful for scripting / no-Java)
racadm can mount images from HTTP/HTTPS/NFS shares to iDRAC (supported in many iDRAC firmware versions). Example:
# mount http ISO (remote racadm)
racadm -r <idrac-ip> -u <user> -p <pass> remoteimage -c -l http://server/share/your.iso
# or NFS
racadm -r <idrac-ip> -u <user> -p <pass> remoteimage -c -l '192.168.1.113:/opt/nfs/OM840.iso'
After the command completes, set the next boot to the virtual media or reboot and use the one-time boot menu.
Notes: some racadm options differ by firmware; consult the iDRAC manual for your exact syntax.
5 — IPMI / Supermicro — step-by-step
A. Web UI (IPMI) — typical flow
- Step 1 – Log in to IPMI web UI at http://<ipmi-ip>/ (or HTTPS).

- Step 2 – Go to Remote Control → Console Redirection or Virtual Media → CD-ROM Image (UI labels vary). Click Launch Console. Depending on BMC and browser, you may download launch.jnlp.

- Step 3 – In console or IPMIView, choose Virtual Storage / Mount Image and point to a local ISO or a web ISO. For Supermicro, there’s usually a Web ISO option to set the image path in IPMI.


- Step 4 – Reboot and boot from the virtual CD/USB device.
B. IPMIView (vendor client) — alternative
- Supermicro’s IPMIView application can mount virtual media, but it frequently requires Java and administrative permissions. If IPMIView fails, try the web UI or use an isolated VM to run older Java versions (safer than changing host settings).
C. License & feature notes
Some vendors or older BMCs may restrict HTML5 or advanced virtual media features to certain license levels or require firmware updates. Community guides show workarounds, but check vendor policy.
6 — Mounting ISOs: local file vs HTTP(S) vs NFS
- Local file (your workstation): The console will upload/stream the ISO from your client to BMC for the session (common with Java method). Easy for ad-hoc installs.
- HTTP(S) share: racadm remoteimage and some BMCs can mount an ISO directly from an HTTP/HTTPS URL – better for automation and avoids Java upload. Example: racadm remoteimage -c -l http://server/iso/installer.iso.
NFS share: Some iDRAC versions accept user@host:/path/iso NFS mounts via racadm (good for large ISOs and repeatable installs).
7 — Common problems & fixes
Problem: Console download launches launch.jnlp or Java fails to run
Cause: Many browsers no longer support Java applets; JNLP/Java Web Start may be blocked or incompatible.
Fixes:
- Use vendor HTML5 console if available (iDRAC9+ typically).
Run Java/JNLP inside an isolated VM with a supported Java 8 JRE (minimize host security exposure). Netrouting and community guides recommend using dedicated VMs for IPMI access.
Problem: Blank screen or lost KVM during boot
Cause: Incompatible Java, firewall blocking VNC/console ports, or BMC bug.
Fixes: Open required BMC ports, try the HTML5 console, update BMC firmware, or use IPMIView. Check vendor KB for blank screen workarounds.
Problem: Virtual media disconnects during install / slow transfer
Cause: Unreliable network, client sleep/hibernation, or the console session closing.
Fixes: Use HTTP(S)/NFS remote image mount (racadm) rather than streaming from your desktop, ensure your workstation doesn’t sleep.
Problem: Feature missing / “mount” greyed out
Cause: Firmware or license limitation, lack of permissions, or legacy BMC.
Fixes: Verify firmware supports virtual media, update BMC, or check vendor licensing & admin privileges. Community posts note that some Supermicro features differ by firmware.
8 — Security considerations & best practices
- Treat BMC credentials like root: store securely and rotate regularly.
- Use HTTPS and secure networks when mounting ISOs from web shares. Prefer HTTPS over HTTP.
- Avoid running Java on your main workstation; prefer an isolated VM when Java is required. Guides explicitly recommend an isolated environment rather than changing system-wide Java security settings.
- Update BMC firmware to fix security bugs and improve virtual media functionality.
9 — Troubleshooting quick commands & checks
iDRAC (racadm) examples
# mount HTTP ISO (remote)
racadm -r 192.168.1.100 -u root -p calvin remoteimage -c -l http://10.0.0.1/isos/ubuntu.iso
# unmount (if needed)
racadm -r 192.168.1.100 -u root -p calvin remoteimage -d
(Exact flags vary by firmware — check your iDRAC manual for your version.)
IPMI tips
If the IPMI web console downloads launch.jnlp, run it with a compatible Java runtime inside a VM. If IPMIView fails, test alternate browsers, or use the remote racadm/remoteimage methods if present.
10 — Printable checklist (copy/paste)
- BMC IP and admin credentials available.
- Bootable ISO ready locally or on HTTP/NFS server.
- BMC firmware version noted; upgrade if outdated.
- Client can reach BMC IP; firewall ports open (e.g., 443 and VNC/5900 if needed).
- BIOS boot order allows virtual CD/USB.
- If Java required: VM ready with Java 8 JRE.
- Plan for reboots and confirm OOB power control if needed.
Post-install: unmount virtual media and restore normal boot order.
11 — Further reading & authoritative references
- Dell KB: How to use the Virtual Media Function on iDRAC6/7/8/9 (step-by-step GUI).
- Dell RACADM remoteimage documentation (examples for HTTP/NFS).
- Dell video: How to Use Virtual Media in iDRAC9 (short demo).
- Supermicro IPMIView User Guide (virtual storage mounting details).
- Community tips and real-world troubleshooting (mounting web ISOs, Java issues).
Important load-bearing claims (sources)
- iDRAC supports HTML5 virtual console on modern versions and virtual media via the console.
- racadm remoteimage can mount HTTP/HTTPS/NFS ISOs to iDRAC for non-Java installs. (Command examples in the iDRAC manual.)
- Supermicro’s IPMI historically requires Java/IPMIView for KVM and virtual media; that can be fragile on modern browsers. Community guides and vendor manual document this.
- Java deprecation in browsers causes many launch.jnlp/KVM issues; best practice is to use HTML5 consoles or isolated VMs for Java.
- BMC ports (e.g., HTTPS/443 and console ports) must be reachable through firewalls for remote console and virtual media to function.
Final tips & recommended workflow (practical)
- Prefer HTML5 console + local ISO for one-off installs (if iDRAC supports it).
- Use racadm remoteimage with HTTP(S)/NFS ISOs for scripted or repeatable installs (avoid client upload failure).
- If Java is required, run Java/JNLP inside a contained VM (safer) rather than disabling security on your main machine.
- After install, immediately unmount virtual media and reset boot order.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Issue |
Possible Cause |
Solution |
| “Virtual Media Not Enabled” |
License missing |
Verify Enterprise license in iDRAC/IPMI settings; purchase if needed. |
| Mount Fails (Error 0x30) |
Network/Firewall |
Check SMBv1 enabled on shares (legacy IPMI); use HTTP for compatibility. Open UDP 623. |
| ISO Not Bootable |
Corrupt File |
Validate ISO checksum; test locally in VM. |
| Slow Transfer |
Large ISO/Network |
Use compressed ISOs or chunked uploads; prefer local mounting. |
| Java Console Crashes |
Outdated JRE |
Update to Java 8+; fallback to HTML5 if available (iDRAC9). |
| Boot Menu Missing Virtual Drive |
Timing |
Mount ISO before power-on; refresh in console. |
| License Prompt in HTML5 |
Vendor Lock |
Switch to Java console for Supermicro; contact support for key. |
For iDRAC-specific: Check logs under “Maintenance > Troubleshooting.” For IPMI: Review event logs in web UI.
Best Practices
- Security: Use HTTPS only; enable two-factor auth. Unmount media post-use to prevent unauthorized access.
- Performance: Mount ISOs <2GB; use Gigabit LAN. For fleets, script with Redfish API (iDRAC10+).
- Testing: Validate in a lab VM first. Backup boot config.
- Alternatives: For automation, integrate with tools like Ansible or Dell’s iDRAC RACADM CLI.
- Vendor Notes: iDRAC excels in Dell ecosystems; IPMI for mixed hardware. Update firmware quarterly.
Conclusion
Mastering virtual media in iDRAC and IPMI empowers you to deploy custom OSes efficiently, minimizing physical interventions and accelerating IT ops. Whether provisioning a Proxmox cluster or a custom Linux build, these tools bridge the gap between remote management and hands-on control. Start with the prerequisites, follow the steps meticulously, and leverage troubleshooting for smooth sails. For vendor-specific tweaks, consult official manuals – your server awaits its new OS.