A practical, end-to-end guide for building reliable, scalable, and production-ready storage
Ceph on Proxmox VE is often perceived as complex at first glance, but when implemented correctly, it becomes one of the most powerful storage solutions available for virtualized environments. For teams running dedicated servers, Ceph removes the dependency on external SANs while delivering high availability, scalability, and resilience.
This guide provides a clear, technical, documentation-style walkthrough – covering planning, hardware requirements, networking, installation, configuration, and operational best practices – so you can deploy Ceph confidently in real-world production environments.
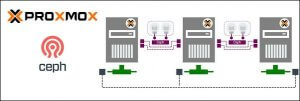
Table of Contents
Ceph is a distributed storage platform designed to store data reliably across multiple nodes while automatically handling replication, recovery, and scaling.
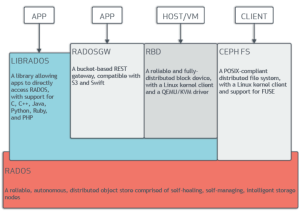
Ceph provides three primary storage types:
Proxmox VE integrates Ceph directly into its management layer, allowing administrators to create and manage shared storage without relying on NFS or iSCSI. This tight integration simplifies deployment while enabling advanced features such as live migration, HA, and automated recovery.
Ceph is most effective when deployed in environments that can fully leverage its distributed design.
Ceph is well suited when:
Ceph may not be suitable when:
Understanding these boundaries helps avoid unnecessary complexity.
Each Proxmox node must provide sufficient compute and memory resources to support both Ceph and virtual machine workloads.
| Component | Minimum | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Nodes | 3 | 5+ |
| CPU | 8 cores | 16–32 cores |
| RAM | 32 GB | 64–128 GB |
| OS Disk | SSD | NVMe |
A general guideline is to allocate approximately 1 GB of RAM per 1 TB of raw Ceph storage, in addition to memory required for the host OS and VMs.
Ceph stores data using Object Storage Daemons (OSDs), each typically mapped to a single physical disk.
Key requirements:
Common disk roles:
Operating system disks should always be separate from Ceph storage disks, and disk types should not be mixed within the same pool.
Ceph is heavily dependent on network performance, especially during recovery and rebalancing operations.
Minimum configuration:
Recommended configuration:
Proper network design is critical to maintaining consistent performance.
Separating Ceph traffic from VM traffic prevents storage operations from impacting guest workloads.
Example configuration:
| Bridge | Purpose | Example Subnet |
|---|---|---|
| vmbr0 | Public / VM traffic | 192.168.1.0/24 |
| vmbr1 | Ceph cluster traffic | 10.10.10.0/24 |
This separation improves recovery speed, reduces congestion, and increases overall cluster stability under load.
Before installing Ceph, all Proxmox nodes must be correctly prepared to ensure a smooth deployment.
Each node should:
Disk readiness must also be verified:
lsblk
OSD disks must be empty, unmounted, and free of partitions or filesystems.
From the Proxmox web interface:
This installs all required Ceph components.
Ceph monitors maintain cluster state and quorum.
An odd number of monitors ensures quorum reliability.
Ceph managers handle metrics, dashboards, and background services.
In modern Proxmox versions, managers are created automatically and require minimal configuration.
Define network ranges used by Ceph:
Public Network: 192.168.1.0/24 Cluster Network: 10.10.10.0/24
This ensures traffic is routed over the correct interfaces.
OSDs are created directly from the Proxmox interface:
Each disk becomes an independent storage unit within the cluster.
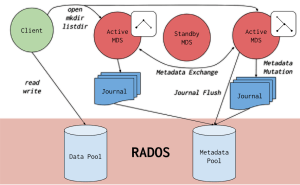
Ceph pools define how data is stored and replicated.
Key parameters:
Typical pool layout:
| Pool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| rbd | VM disks |
| rbd-fast | High-performance VMs |
| backups | Backup storage |
Pools are added to Proxmox under Datacenter → Storage → RBD.
Performance tuning ensures Ceph operates efficiently under load.
Key practices include:
CRUSH rules should be used to separate disk classes so data is placed only on appropriate storage media.
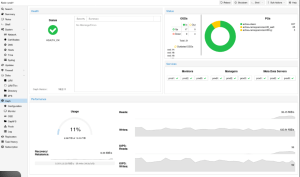
Ongoing monitoring is essential for cluster stability.
Available tools:
Administrators should regularly monitor disk usage, recovery operations, network latency, and cluster warnings.
Ceph protects against hardware and node failures through replication, but it is not a backup solution.
Ceph handles:
Ceph does not replace:
Always combine Ceph with snapshot schedules and external backup systems such as Proxmox Backup Server.
Frequent issues include:
Avoiding these pitfalls significantly improves long-term stability.
Deploying Ceph on Proxmox VE dedicated servers enables a self-healing, scalable, enterprise-grade storage platform without external storage dependencies. When designed with the right hardware, networking, and pool strategy, Ceph delivers consistent performance, resilience, and flexibility for modern virtualized workloads.
If you’re unsure how to size or design your Ceph cluster, you don’t need to figure it out alone – Netrouting engineers are happy to help you plan a setup that fits your workload and growth needs.
